This article establishes what Supported References are, Formula terms and gives examples with explanations for common Formula used within Groundplan.
Summary Notes
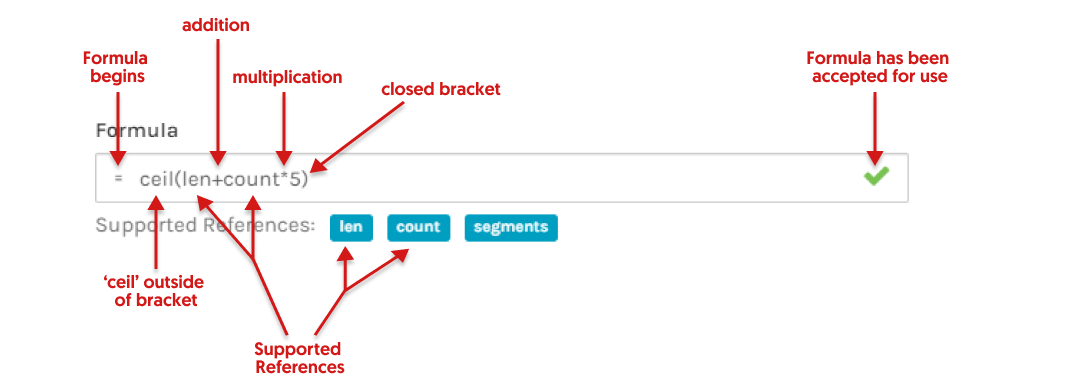
- All Formula must start with an equal sign (=) and include one of the Supported References associated with the Measurement.
- Either whole or decimal numbers can be used.
- Groundplan works in metres (feet for imperial customers).
- Parts and Labour may follow our Grouping rules although Formula is not included within the rules.
- Measurement Parts and Labour article gives step by step instructions to implement Formula.
- Groundplan Formulas follow the PMDAS Rule.
ie: Parentheses (brackets) followed by multiplication, division, addition then subtraction. Calculations within brackets are prioritised. The Totals after any Formula is applied to a Part will be displayed in the bill of materials on the Quantities tab.
| Term | Explained |
|---|---|
| + | Addition |
| - | Subtract or create a negative total |
| * | Multiply (SHIFT 8 to create a * ) |
| / | Divide |
ceil(x) |
Rounds the total (x) and/or Formula inside the brackets up to the nearest whole number. |
floor(x) |
Rounds the total (x) and/or Formula inside the brackets down to the nearest whole number. |
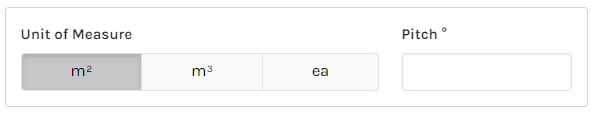
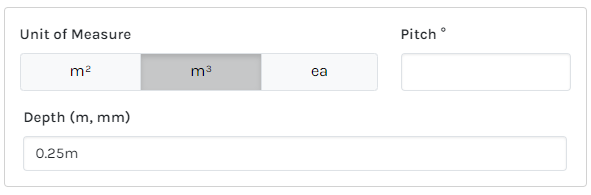
| Unit of Measure | Displayed on the bill of materials and represents the Part being quantified. Some examples include ea, bags, sheets, rods, pipes, m, m², m³. (Supported references will not reference this UOM for calculations). |
Supported References
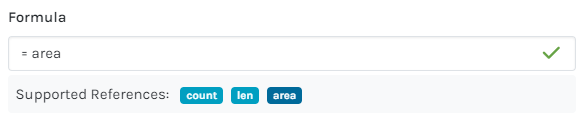
Formulas for Parts within a Measurement include related Supported References. These References vary according to the Measurement type (Count vs Length vs Area). Each Formula must contain a Supported Reference/s to be accepted.
Support References can be used in conjunction with Excel-type Formulas to calculate Parts and/or Labour for a Measurement.
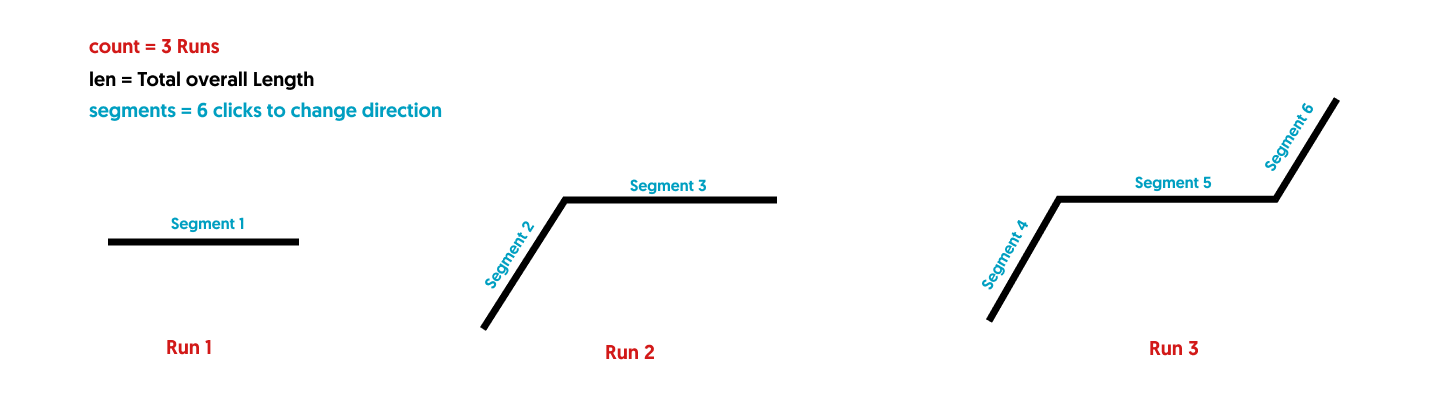
Count Measurement Parts Supported References
How Count Supported References correspond to a Plan:

Count Formula examples
| Formula | Explained | Unit of Measure |
|---|---|---|
=count*8 |
For every Count, multiply the item by 8 metres |
m |
=count*5/100 |
For every Count, allow 5 items divided by 100 (or amount in a bag) |
bags |
= -count |
Create a negative Count |
ea |
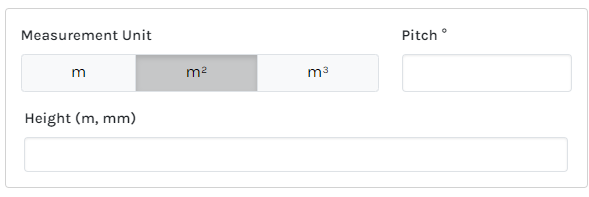
Length Measurement Parts Supported References
How the main Length Supported References correspond to a Plan:
| Length Measurement Unit of Measure (UoM) | Part Supported References | |
|---|---|---|
 |
▶ |
 |
 |
▶ |
 |
 |
▶ |
 |
Length Formula examples
| Formula | Explained | Unit of Measure |
|---|---|---|
=len/6 |
Total length divided by 6, (counting one length every 6 metres) |
lengths |
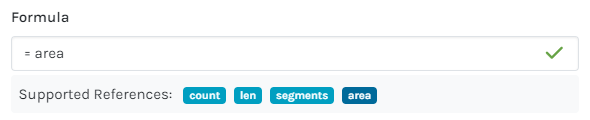
=len*2.4 |
Total length multiplied by height OR depth |
m² |
=ceil(len*2) |
Total length multiplied by 2 and rounded up to the next whole number (ceil) |
m |
=segments*2 |
Each time clicked to change direction multiplied by 2 items along each segment |
ea |
=len+count*5 |
Total length add an additional 5m for each run |
m |
=ceil(len*2.4/2.88) |
Total length multiplied by the height and divided by the area covered by a product rounded up to the next whole number (ceil) |
sheets |
=(len/1.5)+count*2 |
Total length divided by how often a post is (1.5m) and add for each run 2 extra posts (for each end) |
posts |
=volume*1.10 |
Volume multiplied by 10% wastage |
m³ |
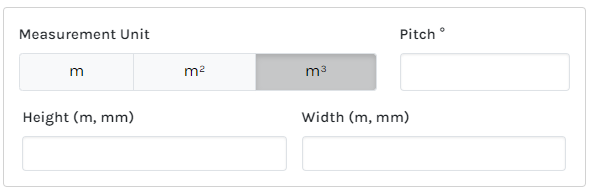
Area Measurement Parts Supported References
How the main Area Supported References correspond to a Plan:
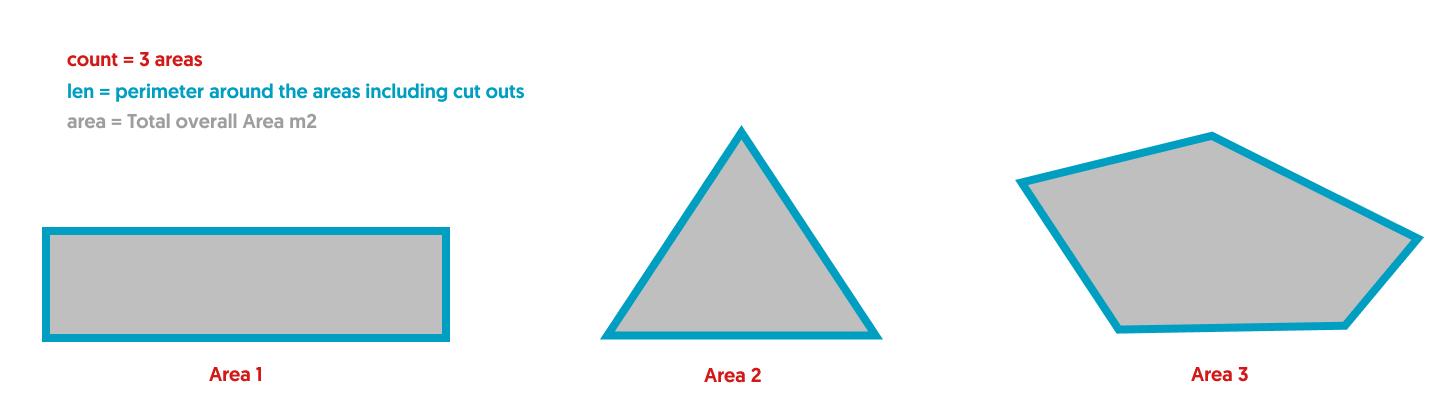
| Area Measurement Unit of Measure (UoM) | Part Unit of Measure (UoM) choices | |
|---|---|---|
 |
▶ |
 |
 |
▶ |
 |
 |
▶ |
 |
Area Formula examples
| Formula | Explained | Unit of Measure |
|---|---|---|
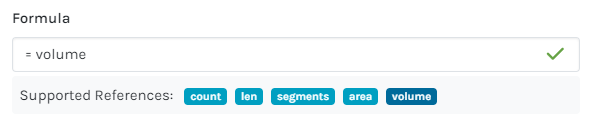
=area*1.5 |
Area multiplied by height OR depth |
m³ |
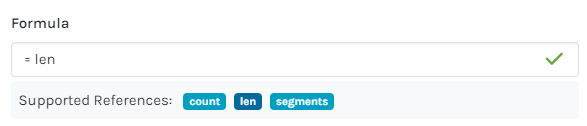
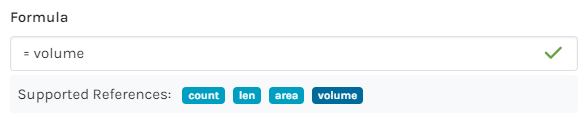
=len |
Perimeter of the area |
m |
=ceil(len/6) |
Perimeter of the area (including any cut outs) divided by 6m lengths rounded up to the next whole number |
lengths |
=area+(len*0.2) |
Area added to (perimeter multiplied by 200mm high) |
m² |
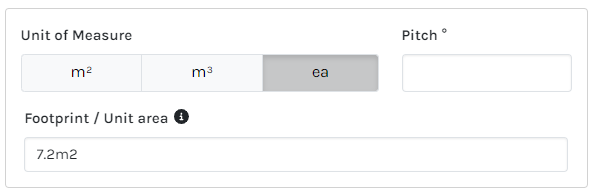
=area/7.2 |
Total area divided by the area of a sheet / product (7.2m2) |
sheets |
=area*4/100 |
In each m² there are 4 items required divided by the amount in a bag |
bag |
=count |
Each area created |
ea |
=volume*1.10 |
Volume multiplied by 10% wastage |
m³ |
=area*1.10 |
Total area multiplied by 10% wastage |
m² |
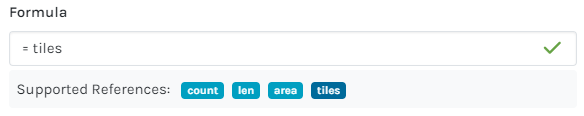
=ceil(tiles) |
Total sheets size populated then rounded up to the next whole number (ceil) |
sheets |
To note:
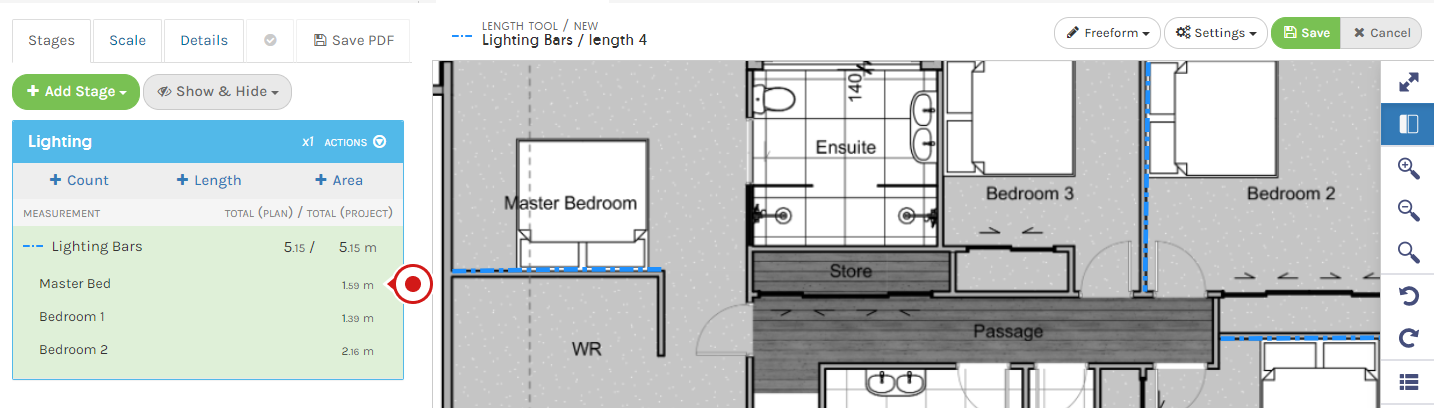
Singling out individual Length / Areas to apply Formula to is not supported in Groundplan.
For example in the image below, applying Formula to the length measured in the Master Bedroom only is not possible.
Length and Area Formulas apply to all Lengths / Areas created within a Measurement. For this particular example, a separate Measurement would need to be created for the Master Bed and then apply the Formula required.
For further information on specific industry examples, please consult the following articles:
- Construction Formulas
- Electrical Formulas
- Landscaping Formulas
- Painting Formulas
- Plastering / Insulation Formulas
- Plumbing Formulas
- Roofing Formulas
Currently, Groundplan does not support "IF" rules in Formula.
eg.
IF (area<160,108, (area/2.22)+36)
Explained: If the area of the slab is greater than 160m2, the total labour hours for a standard slab is 108hrs. Otherwise, the labour is calculated as area/2.22 + 36hrs
We suggest using a program such as Excel for these Formula calculations.
For Formula assistance, please reach out to Support. Go to: Help > Send us a Message.
Organise your session today! Click Help > Send us a Message and ask to book in for free training.
Trainers can assist with:
- Workflow solutions
- Time-saving tips
- Making sure you're getting the most out of your subscription
If you've accessed your free training and need further Support, reach out to book a 1 or 2 hour paid session.